OpenTCS Core Architecture and Basic Concepts Explained
OpenTCS Basic Structure and Core Concepts
This article introduces the core architecture and basic concepts of OpenTCS.
Core Architecture Overview
OpenTCS adopts modular design, mainly including the following core components:
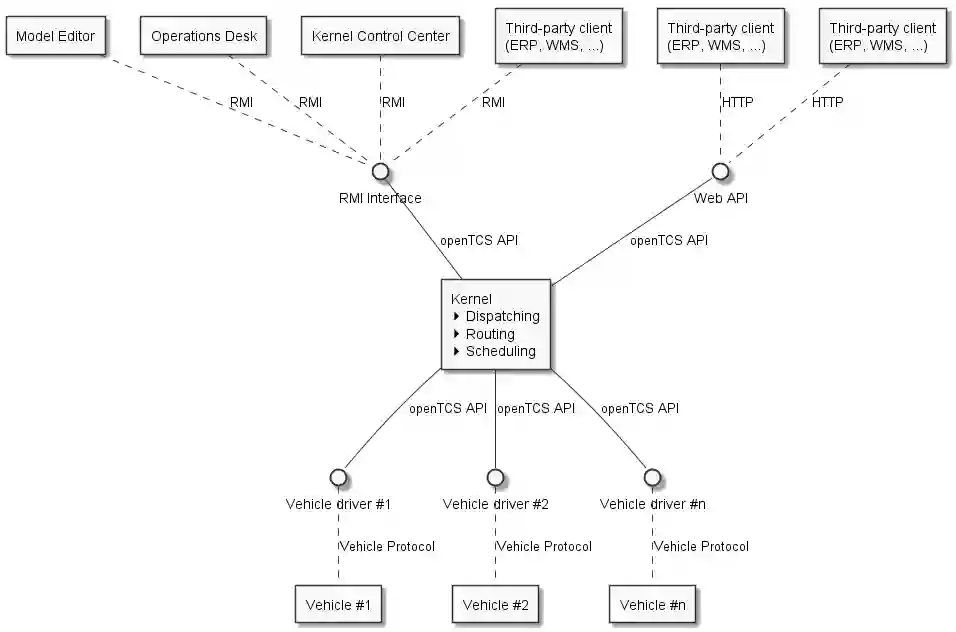
Core Component (Kernel)
Kernel Functions
- Vehicle peripheral control through vehicle drivers and other driver programs, directly controlling other devices via HTTP or TCP custom messages.
- Providing external HTTP interfaces and RMI interfaces (Java remote RPC calls) for external programs to call Kernel methods or access data.
- Order Dispatching Management: How to allocate vehicles when customers require moving something from A to B.
- Routing Calculation: How to perform vehicle movement routing based on shortest path algorithms, such as distance-based, edge weight-based, using Dijkstra algorithm or A* algorithm processing.
- Scheduling Control: Related resource scheduling control when vehicles actually execute tasks. Can lock and exclusively occupy certain resources, such as paths and points.
Research Areas Involving Kernel
- Extending a type of vehicle or peripheral and establishing control communication with them to achieve compatibility with new devices.
- Developing external automation programs that actively control Kernel through HTTP or RMI, achieving decoupling of vehicle scheduling and avoiding direct hard-coded vehicle operations.
- Customizing more efficient order allocation strategies that are better than default strategies.
- Customizing routing calculation methods for better, lower-cost pathfinding for vehicles.
- Customizing scheduling control algorithms for better resource locking and releasing, improving order transport volume per unit time.
What Kernel Cannot Achieve
- Cannot perform precise simulation of real-world scenarios. Kernel only recognizes specific Points, Paths, and specific destinations (Locations). Therefore, specific abstract definitions must be designed based on field conditions.
- Cannot specifically control vehicle movement trajectories. Kernel only tells vehicles they should move from point A to point B; how vehicles plan their movement trajectory from A to B belongs to the vehicle hardware's own scheduling and modeling control.
Model Editor
Built-in Java Swing-implemented map editor for OpenTCS default map editing; detailed explanation not expanded here. Main functions:
- Edit maps, save maps to local XML files, or load maps from local XML files.
- Upload maps to kernel for kernel to recognize the latest map configuration.
Kernel Control Center
Built-in Java Swing-implemented core control console for controlling basic states of vehicles and peripherals. Main functions:
- Enable or disable specific vehicles or peripherals.
- Switch driver programs for vehicles or peripherals.
- Modify parameters of vehicle or peripheral driver programs.
Operations Desk
Built-in Java Swing-implemented operation desk for creating new orders, setting vehicle positions, etc. Main functions:
- Assign and manage order tasks for vehicles.
- Assign tasks to peripherals.
- Real-time monitoring of current operating status.
Core Technology Stack
Backend Technology Stack
- Programming Language: Java
- Dependency Management Container: Guice
- Plugin Extension: SPI mechanism
Visualization Technology Stack
- Programming Language: Java
- GUI Layer: Swing
- GUI Drawing Framework: JHotDraw
- Visual Editing IDE: NetBeans [Eclipse or IDEA can be used for editing and development, but cannot edit Swing component form files because the official source code configures Swing components that are NetBeans-specific, so NetBeans can open them smoothly]
Java Implementation Details Foundation
Need to understand basic concepts of Guice, how to manage and inject dependencies.
Need to understand SPI mechanism, how to automatically discover other JAR packages and automatically take effect.
Need to understand several core Inject extension mechanisms:
- KernelInjectionModule: Core Kernel extension mechanism, subsequent development mainly revolves around this extension.
- ControlCenterInjectionModule: Core controller extension mechanism. If you need to add core controller GUI functionality later, you need to extend according to GUI requirements. If using interface calls instead, generally no need to develop extensions for this module.
- PlantOverviewInjectionModule: Map extension mechanism, generally used for map editor and operation desk extensions, rarely involves extensions.